Understanding RRP Meaning: What Every Retailer Should Know
Pricing can be tough, right? On shopping platforms, it often seems like the same products have a huge disparity in price. With so many sellers and varying strategies, it can be hard to know what a fair price really is. That’s where RRP comes in. So, what is the meaning of RRP, and how can it help you?
Let’s explore these questions together.
RRP meaning: What is RRP?
RRP stands for Recommended Retail Price. This is the price that manufacturers or suppliers suggest retailers use for their products. You’ll often find the RRP displayed on a product’s price tag, packaging, or detailed product page. Retailers can use the RRP as a guideline when setting their own prices.
Besides RRP, several other terms convey a similar meaning. Here’s a quick list:
- List Price: More commonly used in the UK.
- Sticker Price
- Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price (MSRP): More commonly used in the US.
- Recommended Resale Price
- Suggested Retail Price (SRP)
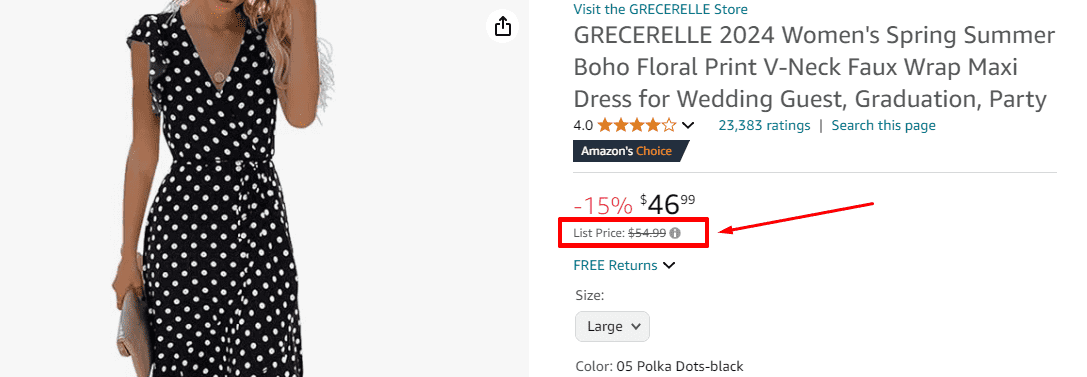
For example, on Amazon, the list price of a new product shown on the product page is provided by manufacturers, suppliers, or sellers. The sellers could change the price freely—the list price is $54.99, but this dress is sold for $46.99.
How to calculate RRP for products?
In most cases, RRPs are given by manufacturers. But if you are selling products you make yourself or purchasing directly from manufacturers who do not mention an RRP, then it will need to be determined manually. Here’s a simple formula:
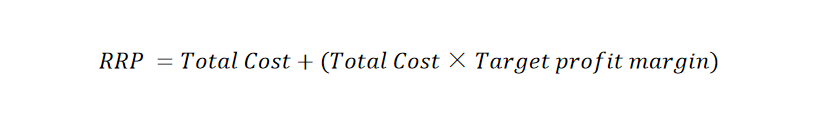
Remember that the sale price is usually less than the RRP, especially if you have plans to offer discounts but you need to ensure that you earn your profit. To account for this, you can use the adjusted formula.
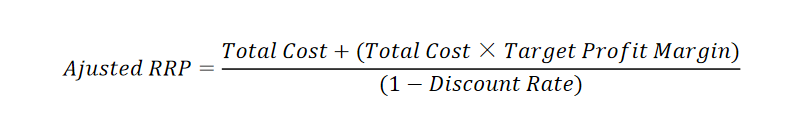
For instance, you buy necklaces from a supplier at $5 and the other expenses including packaging, shipping, tax, and marketing are $20. Therefore you spend $25 as the total cost of the product. If your target profit margin is 40% and you want to offer a 20% discount to your customers, the calculation would be:
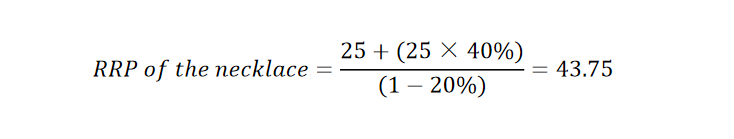
Tip: Remember that RRP is not a mandatory selling price. Retailers are free to set their own prices and adjust them based on their brand situation, market demand, and other factors.
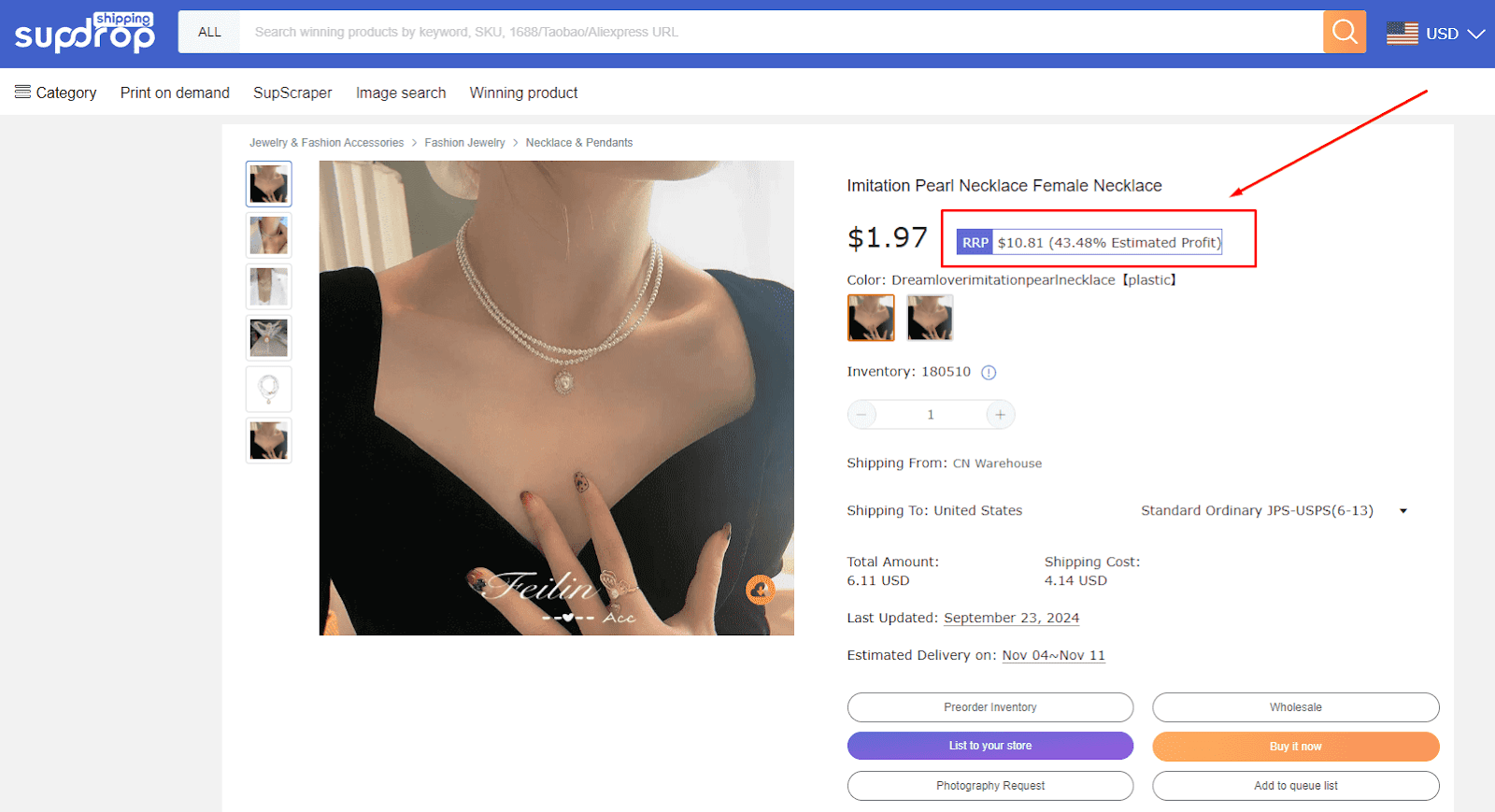
What is the purpose of RRP?
Once you understand how to calculate the RRP for your products, it’s essential to recognize its broader purpose in the retail landscape.
Easy to price a product
One of the primary purposes of RRP is to assist retailers in pricing their products. It serves as a valuable starting point.
Retailers handle hundreds of different products, and it can be challenging to keep track of material costs, market demand, and product valuation for each item. Pricing can sometimes be a tricky issue.
On the other hand, manufacturers are well-acquainted with market demand in their specific fields and know the ins and outs of the products they produce. The RRP they provide is usually based on reasonable pricing. Manufacturers believe that if a retailer sells above the RRP, they may face low sales volume, while selling below it could result in low-profit margins.
However, manufacturers can’t account for the overhead costs of every retailer. Therefore, RRP is just a recommendation—it’s reasonable but not necessarily suitable for every retailer.
Want to price a product perfectly? Check out this: How to Price a Product: A Step-by-Step Guide
Note: In some cases, not every RRP is reasonable. Manufacturers may set a high RRP even when it isn’t realistic, prompting retailers to run promotions or offer discounts.
Avoid vicious competition
Although RRP is not mandatory, it can help curb vicious competition to some extent. With RRP as a reference, retailers gain a better understanding of a product’s reasonable value, making them more cautious in their pricing decisions. This can stabilize market share and reduce the likelihood of cutthroat competition.
Additionally, RRP provides customers with a shopping reference point. When customers have a sense of the market price and see that it is stable, they become less price-sensitive and more focused on quality and brand. As a result, retailers don’t have to rely on lowering prices to attract customers.
Protect brand image
High-end brands often set their RRP above the market average to convey a sense of exclusivity and quality. By maintaining a higher price point, these brands signal to consumers that their products are premium and worth the investment.
By observing the RRP, retailers are useful for the placement of the brand in the market since customers are aware of the RRP and its implications. The consistent pricing of products at the RRP makes the brand more prestigious and can attract quality customers who are willing to pay more for quality. If retailers are often under-pricing the products below the RRP, this may negatively affect the brand image.
When to price above or below RRP?
We know how important RRP is from above. Also, a suitable product price is pivotal for a reseller to reach their selling goals. If you are busy with other tasks like marketing and sourcing, with limited time to focus on pricing, it’s a good choice to use RRP to save time.
Then, how do you use RRP wisely according to different situations? Should you price above or below the RRP?

Pricing below RRP
In most circumstances, the selling price is below the RRP.
- Fierce market: As e-commerce develops, it seems that almost all niches are flooded with hundreds and thousands of sellers. To stand out among them is not easy. Setting a lower price than your competitors may be the most direct and effective way to increase sales volume.
- Promotions: Use discounts to set the price below RRP; the price disparity can encourage customers to buy. Black Friday, Christmas, Halloween, and other holidays are always the best times to offer discounts and promote sales volume.
- Clear storage: Seasonal or holiday products sell well in specific periods. Many outdated products take up your storage space. Pricing these low prices can attract more customers to view and buy the items. In this way, you can effectively free up storage space while still making a profit, even if it’s less than usual.
Pricing above RRP
Pricing above RRP is usually considered a little risky. However, in some circumstances, it may help you earn more profit.
- High market demand and low product quantity: When supply doesn’t meet demand, customers are willing to pay more to get the products, thus pushing prices higher. In this case, pricing above RRP is acceptable.
- A Solid Customer Base: If you have a consistent and loyal customer base, they may be willing to buy items above market prices due to long-term trust and a satisfying shopping experience.
- Brand Image: A well-known brand usually means an excellent reputation, quality control, and great customer service. For example, if you run a business selling luxury goods, customers are inclined to be less price-sensitive. What they consider most is your brand image, and they are willing to pay a premium.
- Value-Added Services: Providing extra services that your competitors don’t offer, such as special packaging, free shipping, or a broader refund policy, can help your products stand out in this market.
What should be noticed when using RRP?

When considering RRP for your pricing strategy, there are a few key tips to keep in mind to ensure you’re making the most of this tool.
Analyzing Competitor Pricing
When you are coming up with your price tag, make sure you have a look around at what similar companies are doing. Understanding their pricing can give you valuable insights into market trends and help you position your products more effectively. What are they charging, over or under the RRP? How does your product meet the quality and features aspects? The analysis will help you make sound choices.
Market Demand and Trends
Pay attention to market demand and seasonal trends. RRP is often based on average market conditions, but those conditions can change. If you notice a spike in demand for a particular product, it might be worth pricing above RRP to maximize profits. Conversely, if demand is low, pricing below RRP could help attract more customers.
Cost Structure Considerations
Always consider your cost structure when using RRP. Just because a manufacturer suggests a price doesn’t mean it will cover your expenses. Make sure to factor in all costs, including shipping, packaging, and marketing. This helps maintain that your prices are competitive but profitable on the other end of the supply chain.
Customer Perception
How your customers view your brand and products. On the other hand, if you are selling luxury products, raising the price could in fact increase their appeal. According to customers’ observations, high prices always mean better quality goods. On the other hand, if your brand established the value attribute, then price undercutting RRP could be more consistent with customer expectations.
Flexibility in Pricing
Finally, please recall that RRP is nothing but a recommended guide. It should be expressive as in it should be able to change from one position to the other. Being able to increase or decrease your prices with timely market, customer, and sales feedback is the right thing to do. Being open to changes can help you stay competitive and responsive to market needs.
What are RPM and MAP?
Aside from RRP, you may have heard about RPM and MAP. These terms are also commonly used in the goods trade. We’ve talked about the meaning of RRP. Here’s an overview of the other two meanings.
RMP meaning
RPM stands for Retail Price Maintenance. It refers to an agreement between manufacturers and resellers that a specific item cannot be sold below a designated price.
For instance, if you wholesale dresses from a supplier and they set a minimum retail price of $100, they may promise a 5% discount on wholesale products if your pricing remains above $100. This means if you sell the dresses for less than $100, you won’t qualify for the discounts. Many retailers may engage in this practice to secure greater discounts, which is a form of RPM, albeit not directly.
While this behavior is intended to maintain brand image, it can harm customers by limiting price competition and preventing them from finding better deals. As a result, RPM is illegal in many countries. Unlike RRP, which is a recommendation, RPM operates more like a mandatory requirement.
MAP meaning
MAP stands for Minimum Advertised Price. This means that manufacturers set a price that sellers cannot advertise below on online platforms or social media. However, products can be sold below this minimum advertised price, and retailers are allowed to provide discount coupons to customers.
Is the MAP policy legal? Yes, in the US, MAP is legal. This policy helps protect brand reputation and prevents negative images from disrupting the brand.
To better understand the differences between RRP, RPM, and MAP, here’s a summary table
| Term | Full name | Definition | Legality |
| RRP | Recommended Retail Price | Suggested price by manufacturers for retailers. | Legal |
| RMP | Retail Price Maintenance | Agreement to keep prices above a certain level, often limiting discounts. | Illegal in many countries |
| MAP | Minimum Advertised Price | Minimum price that sellers cannot advertise below, though they can sell below it. | Legal |
FAQ about RRP meaning
1. What is the RRP in the UK?
RRP stands for recommended retail price. In the UK, it’s often referred to as the list price. This is the suggested price that manufacturers set for retailers when selling their products.
2. Is RRP the actual price?
No, RRP isn’t the actual selling price. It’s merely a suggestion from manufacturers. Retailers have the flexibility to sell products below or above the RRP, which means the actual selling price can vary.
3. Can RRP change?
Yes, RRP can change over time. Manufacturers may update their suggested prices based on market trends, production costs, or other economic factors.
Conclusion
In brief, it is crucial to know the RRP meaning in order to make appropriate pricing plans for your business. Whether you decide to price slightly above or below RRP depends on various factors, and most importantly—the targets of your brand and your customers.
If you are worried about souring, pricing, shipping, and other stuff. Welcome to Sup Dropshipping; with our comprehensive services and a wide range of high-quality products, you can focus on what matters most: growing your business. We take the burden of transportation while you enjoy the full benefits of your profits. Contact us and learn more about how we can help you on your journey today:
About the Author

May
May is a blogger at Sup Dropshipping with over 5 years of experience in eCommerce. May’s passion for eCommerce drives her to stay updated on the latest trends and share her expertise with you through her blog. In her spare time, she likes to read a novel or chat with friends.




Leave a Reply